
Stars
Stars are big balls of very hot gases such as hydrogen, helium,
oxygen, and nitrogen. Stars can contain other elements too, such
as iron and clacium. Stars shine by converting the hydrogen into
helium, release a lot of energy in the form of heat and light,
this works much like the hydrogen bomb, or the atom bomb.
The sun is the most important star to humans because it is so
close to the Earth. The sun supplies Earth with the light and
energy it needs to sustain human life.
Because the sun is so close to the Earth, it is hard for humans
to observe it without special equipment; if humans look directly
into the sun it will damage the eyes. Other stars are much further
away and are easier for humans to look at.
The
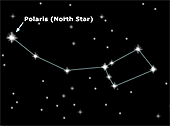
North Star (Polaris): The North Star marks the earth's north
pole. Polaris appears about halfway up the sky to the north, the elevation
above the horizon equal to the observer's latitude. The pole itself, about
which Polaris goes, marks true north, the fundamental direction for inhabitants
of the northern hemisphere that defines the others, east, west, and south.
Polaris also marks the end of the handle of the Little Dipper, the prominent
figure of Ursa Minor. Polaris has the common reputation of being the brightest
star in the sky. The sun at noon marks the meridian, making it possible
to identify due north or south.
Many navigators, particularly the Vikings, relied on the North
Star while at sea.
Sirius:
Sirius is the brightest star in the sky. Sirius is part of
the constellation Canis Major, which looks like a dog in the sky. Sirius
takes the form of the dog's nose in that constellation.That is why Sirius
is commonly known as the Dog Star.
The Egyptians called Sirius "Sothis." The realized
that Sirius's first helical rising occured just before the flooding
of the Nile. A helical rising is when an object in the sky reappears
after a period of absence; its first appearance occurs in the
morning before the rising of the sun. Because of this, the Egyptians
based their calendar on the rising of Sirius in the sky.
1
of 2
next
»

|

|

|

|

|
G A L L E R Y |
View the North Star and Sirius and the constellations they are part
of. [enlarge] |
|
| M
O R E |
"If you stood still in one place all day long, you could tell what time it was by your shadow." Learn about how the solar cycle helps humans to keep time."
|
|
|